How to use Trapezoidal profilers?
Introduction
A trapezoidal profile is a type of motion control trajectory. This method is commonly used in robotics and automation to ensure smooth and controlled movements, minimizing sudden jerks and mechanical stress on the system.
The trapezoidal profile has three distinct phases:
- Acceleration phase: In this phase, there is a positive change in velocity.
- Constant velocity phase: The velocity remains constant, resulting in zero acceleration.
- Deceleration phase: The velocity decreases, resulting in deceleration until the system comes to a stop.
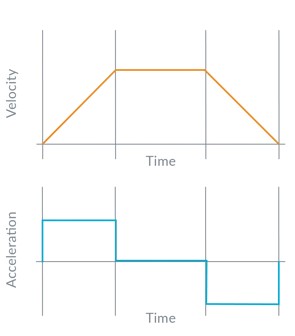
Image from taken fromMathematics of Motion Control Profiles.
With Lightning you are able to create trapezoidal profilers, which provide good performance when traveling distances.
Creating a Trapezoidal Profile
You can create a trapezoidal profile using the TrapezoidalProfile Class.
Check the Trapezoidal Profile Documentation for more information.
But, before creating our profile, we need to determined the maximum velocity and the maximum acceleration for the profile.
The maximum velocity and acceleration doesn´t need to be the maximum achievable. For example, if you want to create a slower profile, you can set the maximum velocity and maximum acceleration to the half of your robot´s maximum velocity and maximum acceleration.
The velocity units must be in (inches/seconds) and the acceleration units in (inches/seconds2) Otherwise, the code will not work as expected.
Once you have determinated the maximum velocity and maximum acceleration, you are ready to create your profile.
void autonomous(){
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile profile (5,1); //5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
}
Setting the target
It´s time to set profile´s target.
For example, if you want that your robot travel 30 inches using the profile you already created, you need to update your profile.
void autonomous(){
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile profile (5,1); //5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
profile.update(30); //Updated for 30 inches.
}
In this way, the profile will calculate the desired velocities for your robot to travel 30 inches.
Moving with Trapezoidal Profile
Finally, you just need to instruct your robot to follow the profile.
void autonomous(){
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile profile (5,1); //5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
profile.update(30); //Updated for 30 inches.
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(profile); //your robot would travel 30 inches
}
Reusing a created profile
You can set different targets to the same profile using the reset() method before setting a new target. This allows you to set multiple distance targets for the same profile without creating a new one.
void autonomous(){
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile profile (5,1); //5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
profile.update(30); //Updated for 30 inches.
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(profile); //your robot would travel 30 inches
profile.reset();
profile.update(60); //Updated for 60 inches.
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(profile); //your robot would travel 60 inches
profile.reset();
profile.update(15); //Updated for 15 inches.
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(profile); //your robot would travel 15 inches
}
Printing velocities
You can print the velocities from any profile to the integrated terminal using the std::cout<< operator.
You must use this operator after setting the target.
void autonomous(){
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile profile (5,1); //5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
profile.update(30); //Updated for 30 inches.
std::cout<<profile; //Print profile velocities.
}
Examples
Using profiles
void autonomous(){
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile profile (5,1); //5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile high_profile (10,2); //10 inches/second, 2 inches/second^2
lightning::TrapezoidalProfile low_profile(2.5,1); //2.5 inches/second, 1 inches/second^2
profile.update(30); //Updated for 30 inches.
//your robot would travel 30 inches.
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(profile);
high_profile.update(24); //Updated for 24 inches.
//your robot would travel 24 inches, using a fasted profile
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(high_profile);
low_profile.update(45); //Updated for 45 inches.
//your robot would travel 45 inches, using a slower profile
my_chassis.move_with_motion_profile(profile);
}
You finished the tutorial! 🎉
You finished the tutorial! Now you can start using trapezoidal profiles in your code.
For more information check the TrapezoidalProfile Documentation.